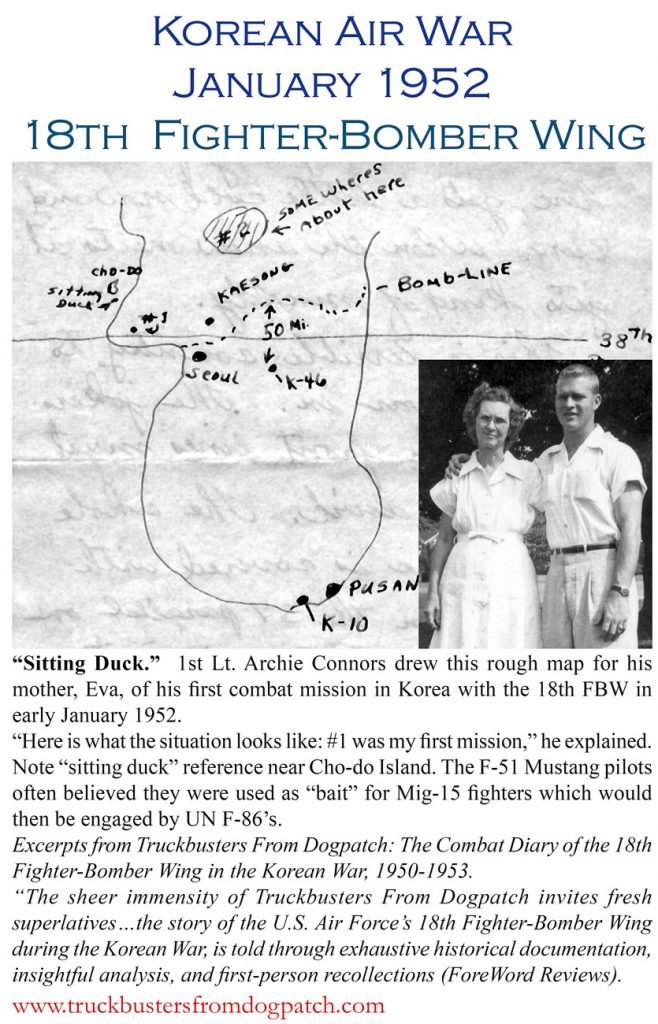
Korean Air War
18th Fighter-Bomber Wing
65 Years Ago
January 1952
During the Korean War (1950-1953) that saved South Korea from occupation by North Korean and Chinese military forces, the U.S. Air Force’s 18th Fighter-Bomber Wing was in combat for 37 months, during which their heroic air-combat efforts flying F-51 “Mustang” fighter-bombers and F-86 Sabrejets are among the most heroic in U.S. military history.
These photographs are excerpted from Truckbusters from Dogpatch: The Combat Diary of the 18th Fighter-Bomber Wing in the Korean War, 1950-1953, a remarkable, 712-page, true-life account of the U.S. Air Force’s 18th Fighter-Bomber Wing from 1950 to 1953. Over 1,000 previously unpublished images from Korean War archives and personal collections are included in Truckbusters.
This service is offered by BelleAire Press to honor those from many countries who fought to protect Freedom and Liberty during the Korean War.
January 1952 Summary
Static, defensive-type ground warfare continued into January 1952. United Nations warships and naval aircraft worked closely with Far East Air Forces to interdict Communist supply networks.
UNF air attacks were countered by active air opposition and increasingly heavy anti-aircraft fire from Chinese Communist and North Korean Forces.
At Panmunjom, UN negotiators labored to achieve an armistice; however “communist intransigence, evasiveness, and procrastination thwarted their efforts.”
UN jet fighters provided protective aerial cover for fighter-bombers and inflicted costly losses on hostile MiG-15s, which made only sporadic attempts to interfere. There was a strong perception among fighter-bomber pilots that they were frequently used as “bait” to entice MIGs into battle. During the month, UN pilots shot down thirty-two MiGs and damaged twenty-eight others.
Although Far East Air Forces “lost only five jets in aerial combat, it saw enemy ground fire destroy forty-four other aircraft. These had been engaged in low-level bombing runs and strafing sweeps.”
The official Air Force chronology makes frequent mention of actions in which jet fighter aircraft, heavy bomber aircraft or rescue helicopters were engaged, but rarely mentions actions by fighter-bomber squadrons flying the now outdated F-51 Mustang aircraft.
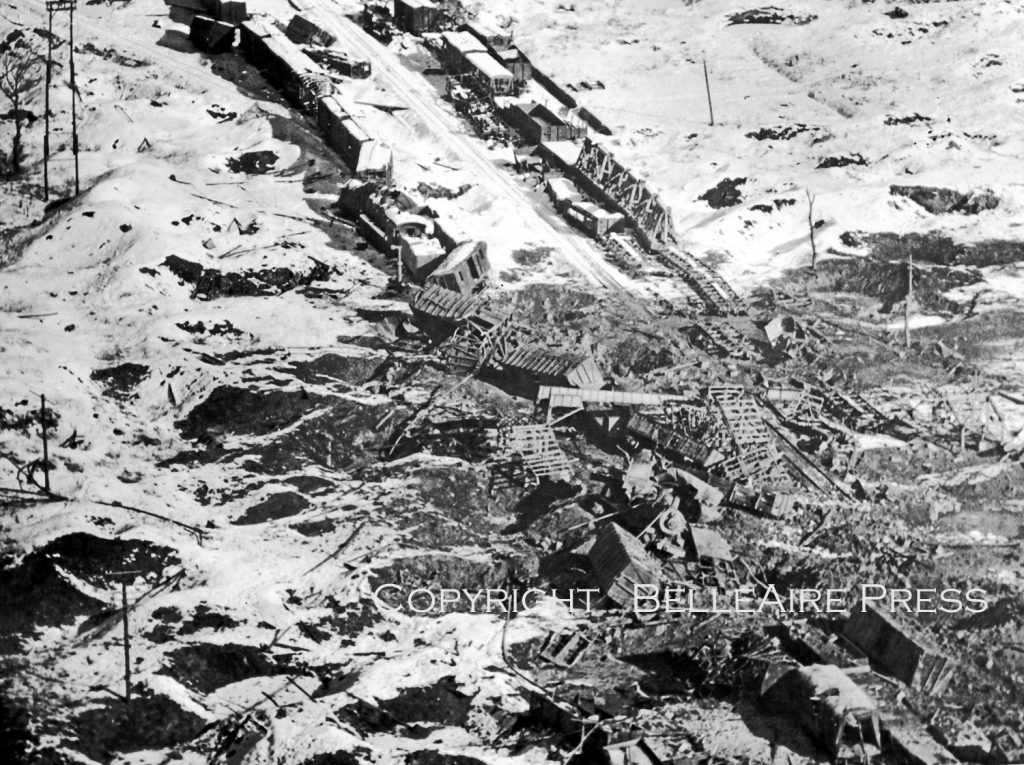
Fifth Air Force tactical strikes were directed primarily against railheads, communication lines, and highways over which the communists moved supplies and equipment to front-line positions. Fighter-bombers concentrated on rail-cutting missions but also provided vital close air support (CAS) for Eighth Army ground forces that included bombing, napalm, and rocket strikes.
Adapted from U.S. Air Force Historical Research Agency. January 2002.


 Truckbusters
Truckbusters